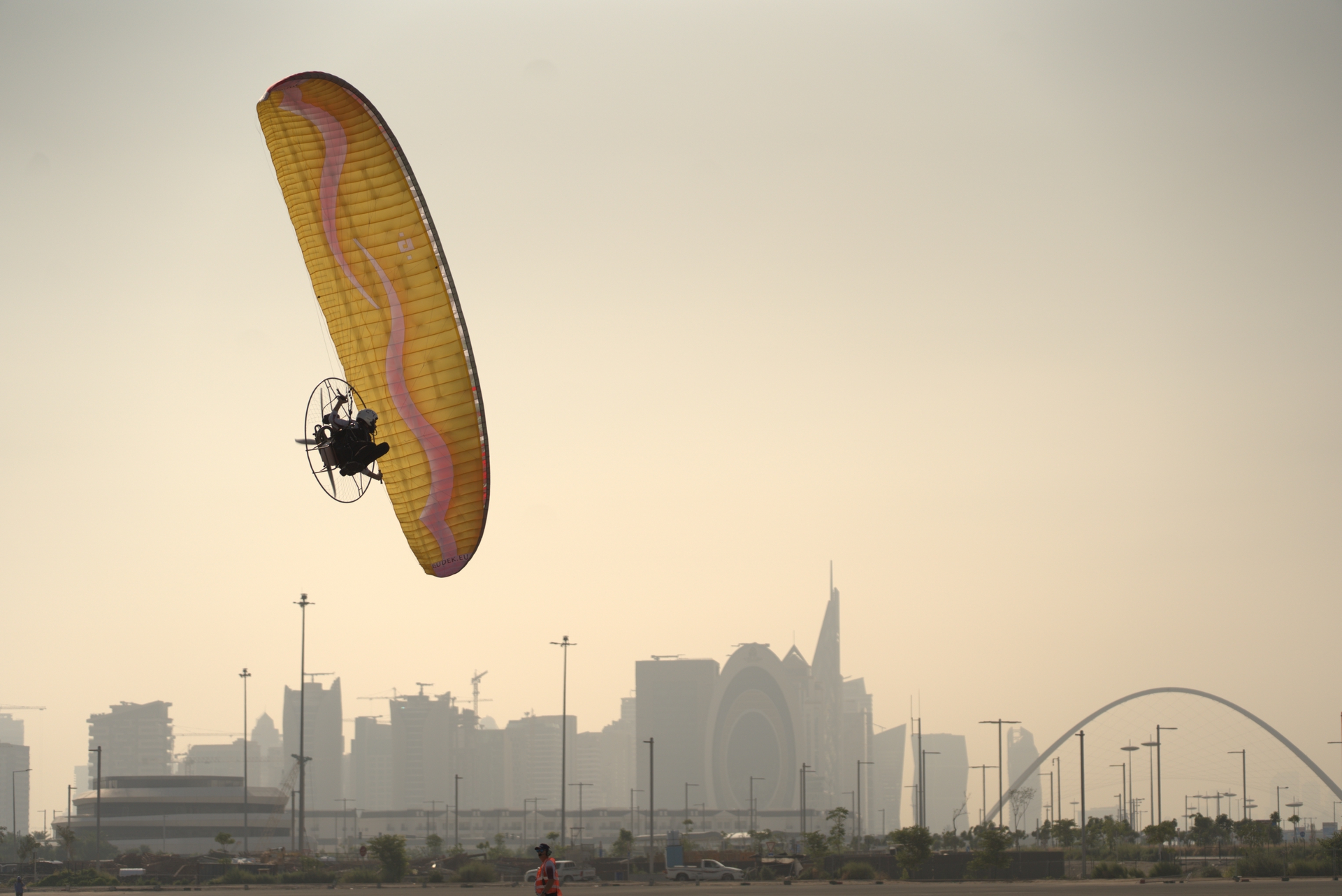
Snake 4
Snake 4
Snake 4 is the newest version of our flagship slalom racing wing.

Design and purpose
Snake 4 is a dynamic slalom wing, highly fast in turns, with exceptional resistance to collapses.
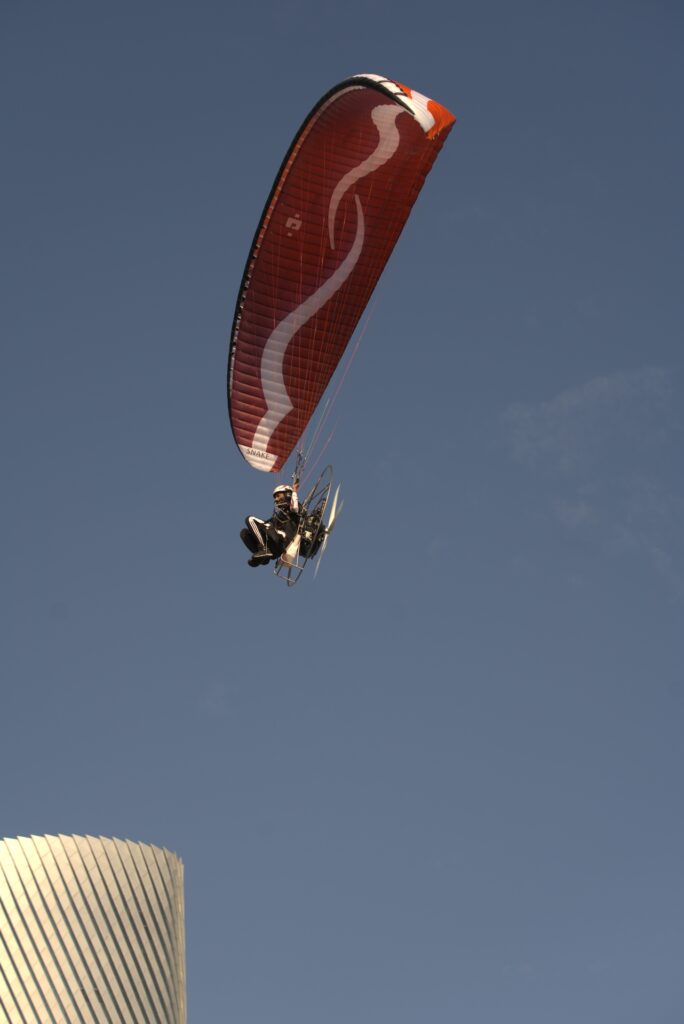

The priority in creating the Snake 4 wasto increase the rigidity of the canopywhile flying at full-speed. The design goalswere achieved by introducing somestructural changes, including:
- modification of the aerodynamic profile
- modification of internal reinforcements
- increasing its tension at the trailing edge
Risers have undergone significant changes. Now they are more narrow than before, with a width of 15mm. The use of additional, bearing blocks resulted in smoother operation when pushing the speed bar. Thanks to the lower weight of the risers and a more clear finishing, the comfort of their use has increased.
In addition, we are expanding the possibilities of Snake 4 by introducing two versions to the market:
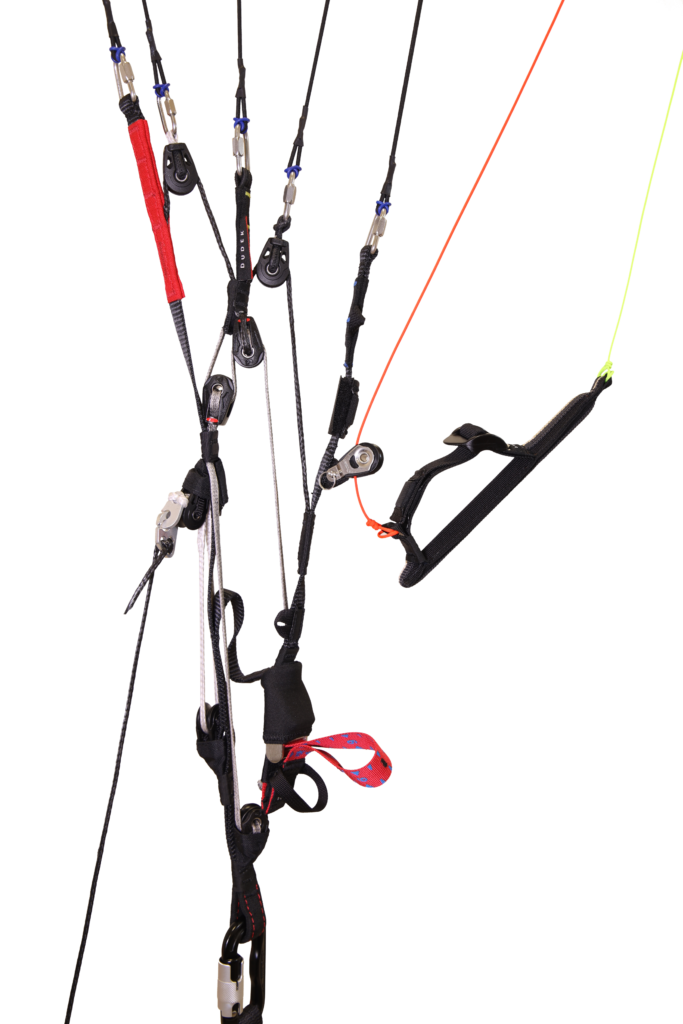
- Standard – risers are equipped with trimmers and have a slightly shorter speed system range to increase safety and enjoyment of the flight for less experienced slalom competitors, as well as for those who do not fly in competition at all. In the “Standard” version, sheathed main lines are used, just as in Snake 3.
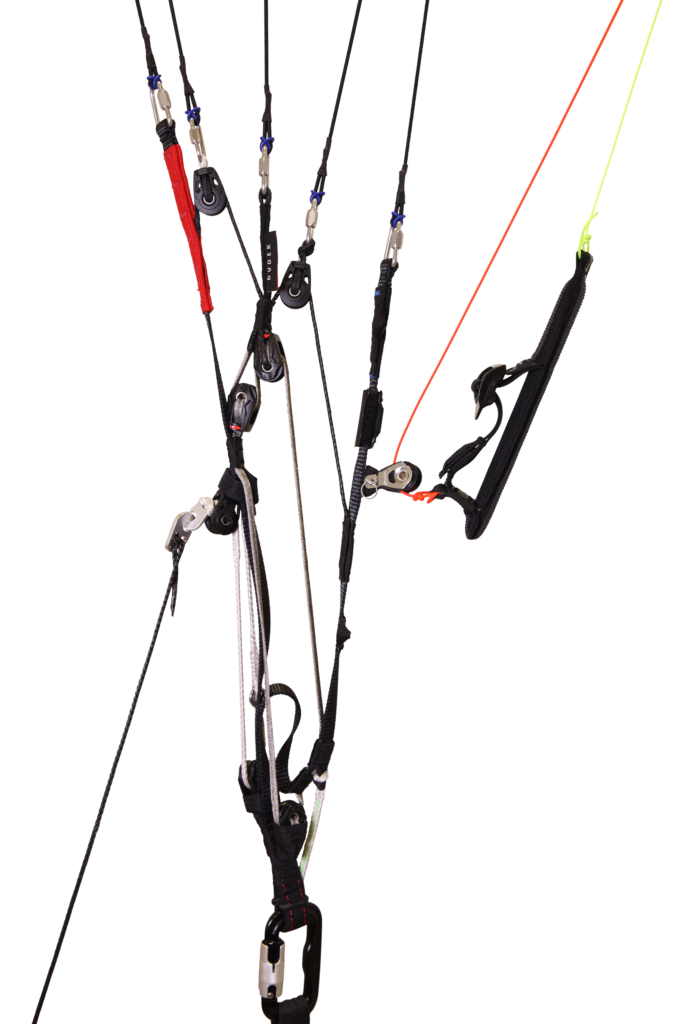
- Pro – risers do not have trimmers and the main lines are unsheathed. It is an uncompromising solution for world-class competition pilots. Pro version is available in sizes 18 and smaller.
——-
It is recommended that Snake 4 pilots have experience in flying wings in the DriftAir class or more demanding categories. Snake 4 will meet all the needs of demanding PPG pilots, and in the Pro version, It becomes the most advanced and precise tool, essential for winning competitions.
More construction details
- Shark-nose (SN) on the leading edge takes care of better aerodynamics of this part of the canopy, as well as higher inner pressure at wide range of the attack angles (meaning airspeed).
- The leading edge is stiffened with synthetic rods of the FET (Flexi Edge Technology), distinctly improving launch quality and guarding against collapses at high speeds.
- In addition Leading Edge 3D system enables a better real representation of the aerodynamic profile and reduces the amount of wrinkles on the fabric in the most important place in terms of lift and air resistance.
- The design features also other effective methods of canopy loads distribution, mediated by most modern sewing technologies.
- Four rows of suspension lines are joined at the risers, equipped with compact yet very efficient tools like trimmers, speed and Power Attack (PA) system.
- Steering system of the Snake 4 is our well known, original solution of 2D steering, this time with new adjustable CHR handle, combining features of both the TCT and TST (Tip Steering Toggle).
- As per our standard, the risers are equipped with three optional positions for the steering pulleys and magnets to choose from. Thanks to all these features, steering operation is straightforward and intuitive.
- Obviously, in some powerpack/canopy configurations considerable amount of torque can appear. To counter this, there is proven in our Warp an automatic TEA system (Torque Effect Adjuster). It works on its own after placing the line on proper side, depending on the torque direction.
- Due to the small number of lines, they were carefully selected to obtain the lowest possible air resistance, while ensuring high strength and resistance to stretching. The upper layer lines, attached to the wing’s suspension points are unsheathed, in the lower layers we use regular sheathed lines.
Snake 4 is manufactured entirely in Europe, at our Polish plant, so that we have total control over its sophisticated production process (using among else the advanced LT (Laser Technology) cutting.
Construction solutions
Technologies, Concepts
Risers functionality
Used Solutions
| “Standard” risers: | “Pro” risers: |
 |
 |
Parameters
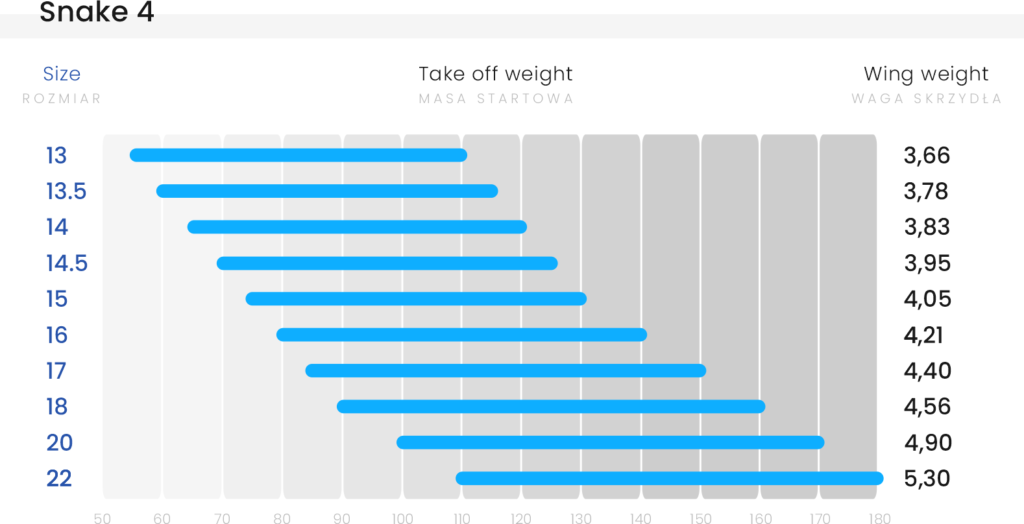
Weight ranges
Technical details
| Snake 4 – sizes | 13 |
13.5 | 14 | 14.5 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 20 | 22 |
| Approval – ULM identification | ||||||||||
| Number of cells | 60 | |||||||||
| Surface area (flat) [m2] | 13 | 13.5 | 14 | 14.5 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 20 | 22 |
| Surface area (projected) [m2] | 11.29 | 11.72 | 12.16 | 12.59 | 13.02 | 13.89 | 14.76 | 15.63 | 17.36 | 19.1 |
| Span (flat) [m] | 8.64 | 8.81 | 8,97 | 9.13 | 9.28 | 9.59 | 9.88 | 10.17 | 10.72 | 11.3 |
| Span (projected) [m] | 7.08 | 7.22 | 7.35 | 7.48 | 7.61 | 7.86 | 8.1 | 8.33 | 8.78 | 9.21 |
| Aspect Ratio (flat) | 5.80 | |||||||||
| Aspect Ratio (projected) | 4.44 | |||||||||
| Distance pilot to wing [m] | 5.04 | 5.14 | 5.23 | 5.32 | 5.41 | 5.59 | 5.76 | 5.93 | 6.25 | 6.78 |
| Total line length [m] | 238.6 | 243.4 | 244.1 | 252.75 | 257.27 | 266.14 | 274.73 | 283.08 | 299.10 | 308.95 |
| Total take-off weight* [kg] | 55-110 | 60-115 | 65-120 | 70-125 | 75-130 | 80-140 | 85-150 | 90-160 | 100-170 | 110-180 |
| Distance between risers [cm] | 45 | |||||||||
| Weight [kg] | 3.66 | 3.78 | 3.83 | 3.95 | 4.05 | 4.21 | 4.40 | 4.56 | 4.90 | 5.30 |
| Lines | 2 80001: 050; 070; 090; 130; 190 / Technora: 140 & 190 & 280 / Dyneema: 350 | |||||||||
| Fabric | Dominico tex 41 g/m2; Porcher Sport 32 g/m2; Dominico tex Hard 41 g/m2; SR Scrim, SR Laminate 180 g/m2 | |||||||||
* The basic rule is to choose the wing size so the take-off weight is in the middle of the weight range. Less weight on the wing (lower range take-off weight) can be considered for foot take-off, when flying in calmer conditions, or when we want to improve economy. More experienced pilots who want to fly dynamically, have higher speed and fly in more demanding wind conditions can consider greater wing loading (take-off weight in the upper range). This is a common option among trike users.
Note – the canopy significantly changes its behaviour with increasing wing loading. The greater the loads, the greater skill and concentration of the pilot are required.